What are Custom GPTs and Why Do They Matter?
Most people use ChatGPT like this:
They ask a question/make a request, get an answer, react… and stop.
That’s not wrong, but it’s also why ChatGPT can feel inconsistent, frustrating, or forgetful. A Custom GPT is simply ChatGPT with instructions added ahead of time, so it already understands:
-what you’re trying to do
-how you want answers written
-what to focus on
-what to avoid
It’s a way to use ChatGPT that eliminates the need for you to explain yourself every time. Think of it as training ChatGPT the way you’d train a new employee.
Why Regular ChatGPT Can Feel Frustrating
If you’ve ever stared at a ChatGPT reply and thought:
-That’s not what I meant.
-Why did it answer like that?
-It worked yesterday, but not today.
-I’m tired of rewriting the same prompt.
You’re not alone.
Regular ChatGPT starts every conversation from scratch. It doesn’t know your style, your goal, your audience, what you liked last time, etc., so you end up doing the heavy lifting every time. It’s not only exhausting, but it also wastes time and kills enthusiasm fast.
When you create a Custom GPT, you give ChatGPT context and guardrails ahead of time, before you ever type a prompt. You give it clear instructions in plain English once. Instead of guessing, a Custom GPT responds the way you want by default.
The beauty of this is that anyone can create a Custom GPT, or a Gem in Gemini. You don’t need to know how to code, have a technical background, or learn fancy AI jargon. You’re not programming anything. If you can explain something to a coworker, you can create a Custom GPT.
Simple way to think about it:
Regular ChatGPT = talking to a stranger every time
Custom GPT = talking to someone who already knows exactly what you want
Giving a Custom GPT “Knowledge”
A knowledge file is simply a document you give to a Custom GPT so it doesn’t have to guess.
That’s it.
Instead of relying on general information or guessing, your Custom GPT will reference your actual material the way a human would flip open a folder or cheat sheet before answering a question.
You add documents, PDFs, spreadsheets, and images to a CustomGPT and tell it how to use them. Examples of knowledge files that work best for radio:
-Guidelines
-Examples
-FAQs
-Style Preferences (like writing or branding guides)
-Standard language, terminology, phrases
-Audience profiles (think: who is this for?)
Knowledge files don’t need to be perfect or polished; they just need to be accurate. Be mindful that well-organized, concise documents perform better.
When the information in any of your knowledge files changes, just open your Custom GPT, delete the current one, and upload the new version, which will be used from that point on. Gemini makes it even easier by letting you connect Google Docs as knowledge files for Gems. That way, when you update the Google Doc, your Gem has been updated, too.
Custom GPTs and Gems give you the advantage of specialization, consistency, and speed.
Taking the time to learn how to create and use them effectively is a learned skill.
It’s not the AI’s magic that takes you to the next level; it’s yours.

Creating a Custom GPT
As tempting as it might be to start creating a Custom GPT on the fly, it will only cause you headaches and cost you time down the road. Organize a plan in writing, starting with what success looks like. Imagine it’s a co-worker helping you accomplish a task or learn something.
What does this GPT do?
What are the steps involved?
What should its response look like, or how should it be formatted?
What information will it need?
What important details should it give special attention to?
Are there things it should avoid, or never do?
Keep it simple and focused on a single goal. Be straightforward and direct in your planning, and it will carry over to the instructions you give to the Custom GPT.
Plan First
Getting Started
There are two ways to create your own Custom GPT:
Create: the more guided, chat-style builder (good for getting started fast).
Configure: the “control panel” where you set the exact settings and behavior.
The Create tab is for conversational, guided building, where you tell the GPT Builder what you want in plain English, and it generates the initial instructions and configuration. The benefit of using the Create tab to get started is that once you’ve got the basics of your Custom GPT created, you can switch to the Configure tab to see how the instructions were written.
To ensure your Custom GPT gives you a consistent response and fewer surprises, you’ll spend most of your time in the Configure screen.

Understanding and Customizing Configurations
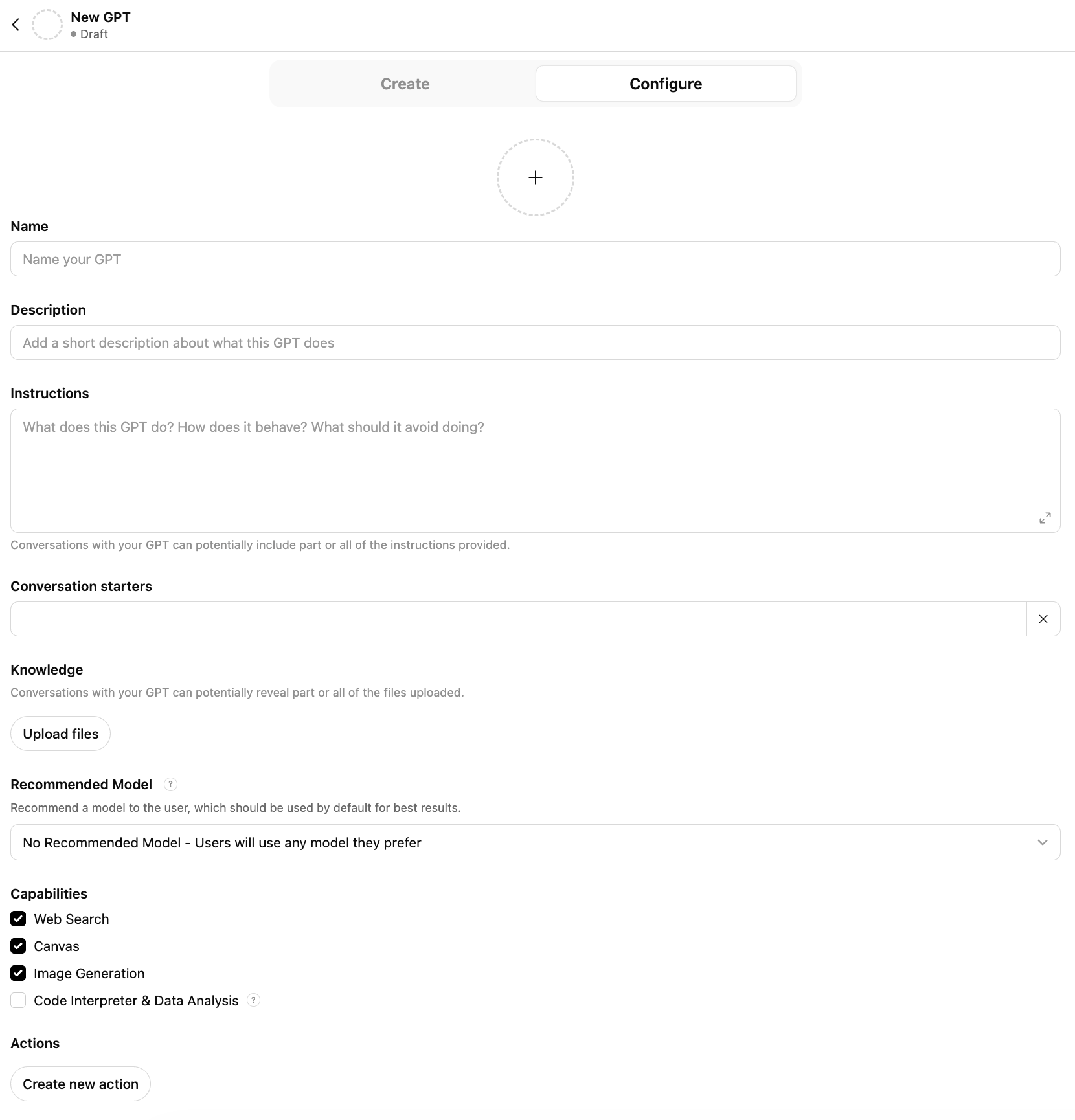
At first glance, the Custom GPT Configuration screen can look intimidating. Lots of fields, options, and terms you may not be familiar with. You might start thinking this is more than you signed up for. It’s not. Here’s what each section really does, in plain English.
GPT icon (the circle with a +)
This is the profile image for your GPT. Useful if you’re making multiple GPTs and want to recognize them quickly. Totally optional, but helpful for organization.
Name
This is what you’ll see in your GPT list. Keep it clear and specific (example: “Short & Clear Email Helper”). If it’s vague (“My GPT”), you’ll forget what it’s for later.
Description
This is a short sentence that explains what it does. Think: “If someone else saw this, would they instantly get it?” Example: “Helps me rewrite emails in a friendly, professional tone: short and to the point.”
Instructions
This is the most important section. It answers:
What does this GPT do?
How should it behave?
How should it use the knowledge docs you’ve attached (if any).
What should its response look like (formatting).
What should it always do/never do?
Here’s a simple starter structure for instructions.
(Advanced structures can be found below.)
Role: “You are a ___ and you help me….”
Goal: “Your goal is to ___.” (What the GPT helps you accomplish.)
Rules: (your special guidelines)
Constraints: Always ____. Never: ____.
Output Format: “Use bullets, keep it short, format as a script, etc.”
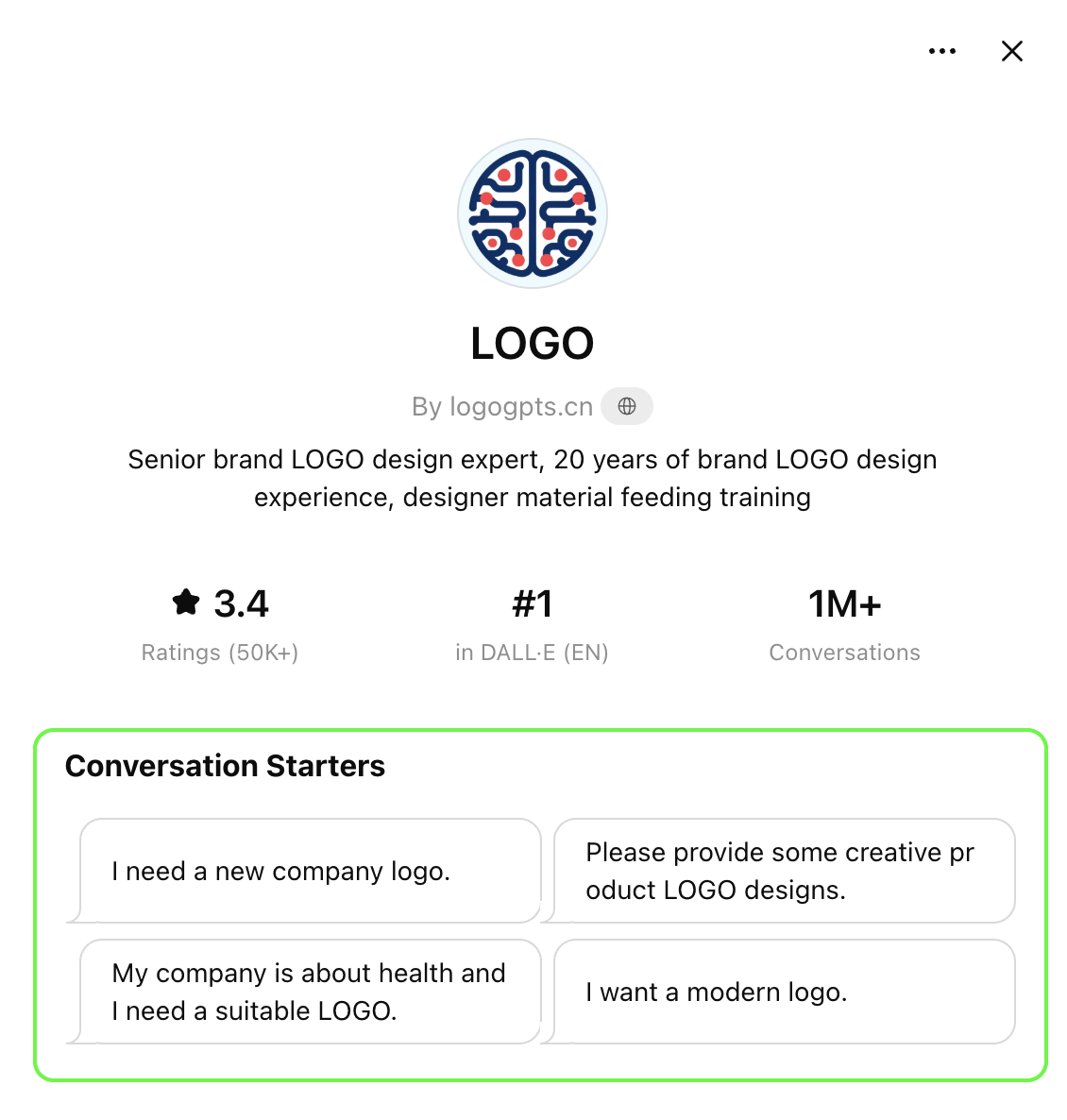
Conversation starters
These are clickable “example prompts” that appear below the name and description of a Custom GPT when it’s opened. They’re pre-set prompts that help the user get started with a single click. They’re great for users used to one-shot prompts. They can also help guide users toward specific outcomes. See examples below and in the image to the right.
Examples:
Rewrite this message to sound friendly but firm: [paste]
Give me five headline options for: [topic]
“Summarize this in 3 bullets: [paste]
Knowledge (Upload files)
This is where you’ll upload and attach the documents you reference in your instructions, such as guides, examples, templates, FAQs, etc., that the Custom GPT will use as you direct. Very useful when you want the GPT to follow style or branding guides or focus its thinking to only use the knowledge you supply (as opposed to what it’s been taught, the internet, chat history, etc.)
Uploading knowledge documents isn’t mandatory. If you don’t upload anything, it will still work.
Recommended Model (dropdown)
This suggests a default model for best results. If you leave it as No Recommended Model, users can still pick whatever they want. If you want more control over the output's consistency and know which model will work best for this Custom GPT’s goals, choosing one can reduce the “it worked yesterday but not today” effect.
Capabilities (checkboxes)
These control what your GPT is allowed to do.
Web Search: can look things up online (helpful for current info; not needed for private/internal work).
Canvas: can create/edit documents or layouts in a canvas-style workspace (handy for drafting).
Image Generation: can create images from prompts.
Code Interpreter & Data Analysis (if enabled): can analyze files, do calculations, and work with spreadsheets/data.
Simple rule: turn on only what you’ll actually use—fewer capabilities = fewer unexpected behaviors.
Actions (Create new action)
This is for connecting your GPT to external tools/services (advanced). Examples include pulling specific data from external databases, sending the GPT’s output to a specific destination, and calling an API. Actions is an advanced option you can skip for now.
GPTs or Gems?
If you use the free version of ChatGPT, you can see and use many of the customized GPTs in the GPT Store; however, creating a Custom GPT requires a paid ChatGPT subscription. ‘Gems’ are a feature/tool found in Google’s AI environment, Gemini. Gems function similarly to Custom GPTs and can be created using a free Gemini account. As of this writing, applying the instructions, templates, concepts, and examples shared here will produce similar outcomes when creating and customizing a Gem.
Most importantly:
You don’t need to fill out everything. You don’t need to get it “right” the first time.
And you’re not breaking anything by experimenting.
A Custom GPT isn’t a technical project: it’s a clarity tool, unlike anything you’ve ever used before.
And when it’s done right, it feels less like “using AI” and more like finally
having AI work the way you expected it to all along.

Review and Improve
Don’t be discouraged if the response from the custom GPT you just created isn’t what you expected. A bit of trial and error is to be expected. That also happens when only humans are involved in any project.
Initiate, activate, review, adjust, retest.
Iteration is part of the process. The difference between making adjustments to a prompt and to a GPT is that each time you adjust the instructions for your Custom GPT, those changes stick. Unlike fine-tuning a single-shot prompt over and over every day, you’re much less likely to get caught on the merry-go-round of fixing one thing only to find out something else that was working before is now a bit off.
We’ve created a detailed example of building, testing, and refining a Custom GPT on the Creating a Custom GPT Step-By-Step page. The example features a Custom GPT created to find news stories with a distinct nature and reframe them individually to suit the different styles of two morning show hosts. The custom GPT's goal is the same one morning shows and morning show producers have had every day for decades.
Imagine creating a Custom GPT that does 95% of the work in a few seconds.
This is where AI is taking us. Yes, it may require a few hours of your time to get things working the way you want. In the end, it’s a fair tradeoff for the hundreds of hours you’ll save in the next year alone. This is what’s possible right now.

Templates + Instructions for Custom GPTs that create Knowledge Documents
Creating a custom GPT to manage tasks and generate content quickly, as you would, means the GPT needs to know and understand what you do. Uploading files containing data, examples, policies, strategies, handbooks, and related materials adds context to GPT’s output. For example, if you want the GPT’s response to reflect and adhere to the guidelines of your station brand strategy, you can upload it to your GPT and reference it in the instructions.
Example: Write all responses in the Station Brand writing style as described in the knowledge document titled Station Brand Writing Style Guide. Be sure to review this document before creating or writing all responses.
Examples of the types of Knowledge documents that add consistency, stylization, differentiation, and personalization to your custom GPT’s output:
Station Brand Identity Style - promos, imaging, web/social content, newsletters
Individual Personality Writing Styles - prep curation, social posts, video scripts, show promo scripts
Target Listener Personas and Value Mapping - station imaging, contesting ideas/promos, localization
Client/Sponsor Brand Guidelines - endorsements, sales remotes, spec spot copy, sales presentations
Station Voice Blueprint - rules of the road to keep the AI from hallucinating or going off-brand
As easy as these are to conceptualize, actually creating one can be challenging. Getting help from the AI itself can be a solid start. But please… whatever you do, don’t merely describe your station, show, or personal style and then ask ChatGPT to create a style guide. That’s asking for trouble. Believe us. We’ve been on the front lines of asking for trouble for years. All for the greater good, mind you.
Creating A Custom GPT That Makes Other Custom GPTs More Effective
After months of testing, refining, breaking, and fixing, and going back to the drawing board, we’ve identified highly effective Custom GPT instructions, constraints, and contexts that build Custom GPTs capable of creating style guides that can be used ask Knowledge documents for other Custom GPTs.
We continue to test new methods, angles, and combinations of AI capabilities in our never-ending mission to make it simple, safe, and wildly beneficial for radio personalities, producers, Program Directors, Promotion + Marketing Directors, and Sales Managers to partner with Lindy Media AI Consulting.
The proof, as they say, is in the pudding. So here’s a giant bowl of it, on us.
Download these Custom GPT instructions to recreate them in your ChatGPT account to generate Brand Identity and Brand Positioning guides you can use as Knowledge documents in the Custom GPTs you make
The downloads have instructions and notes you’ll want to review first. If you get stuck or things don’t seem as easy as we say they are, it won’t cost you a dime to get in touch so we can block off some time to help you get going in the right direction.
The Lindy Media AI Style Architect template is built to help you create an advanced version of a DJ/personality style guide. We’ve developed a two-prompt system that goes beyond summarizing a personality’s style. As we chase down the perfect, or near-perfect, combination of ingredients to build the ultimate AI linguistic profiler, the results from this two-prompt system, created using Gemini, were the best we’ve seen so far.
Heads up: you will need multiple audio performances and their transcriptions of the person you’re creating the Style Guide for. Learn more in the notes and tips section of the Style Architect download.
Special Note:
Downloadable GPT Templates and Instructions that create customized Knowledge Docs

Custom GPT Example and Template Downloads
You'll notice that the output from these free templates sometimes includes information or content you didn’t ask for, like a definition of your target audience, or a 90-day marketing plan.
The best practice: ignore what you don't need, gather what helps, refine, and apply. Customizing and personalizing these templates and Custom GPT instructions won’t get you perfection, but they will get you a few yards from the goal line.
Be wary of the high-noise-to-signal claims that a prompt, custom GPT, Gem, Agent, or any AI tool will produce a 100% accurate, perfectly written, expertly branded, and elegantly formatted output every time.
The idea of sharing these templates is to help you learn how to build your own versions of AI tools and processes that already know what you need before you even use them.
Custom GPTs, Gems, and AI Agents relieve the pain of a well-constructed prompt failing to deliver consistently. They give you your time back and the kind of productivity you’ve been expecting from AI. It's about getting something you can actually use, faster with less effort.
Radio doesn’t need AI to become something else … or some new version that ‘kind of’ resembles what got us here. Radio needs AI so we can do more of what we already do best.
Future-proofing in Radio doesn’t mean becoming more technical. It means becoming more powerful creatively, and AI does precisely that, giving us the tools that finally match the speed, intimacy, and emotional punch that only radio can deliver.
We own that legacy. AI has dropped the power to own that future right in our lap.
Learning to build a Custom GPT is just one of the ways today’s radio people, in every role, can multiply their creative value. We’re building a better playbook because the game is being played faster and faster. The next move is ours.
This is where we are.